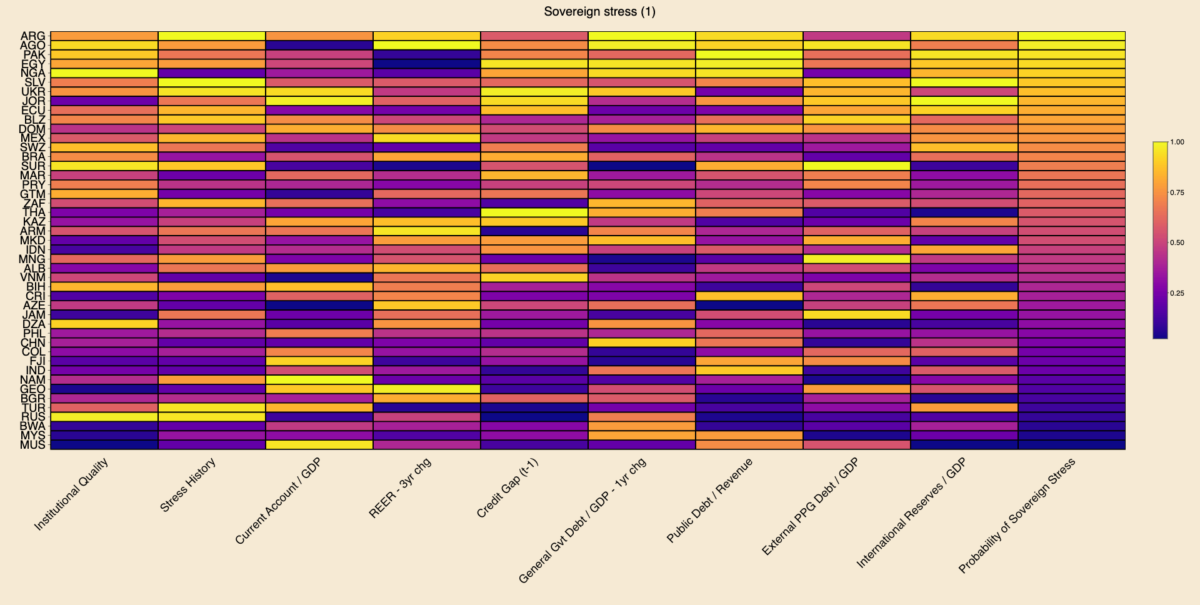
Today’s charts are an update of the Sovereign Vibe sovereign debt stress tracker initially released in 2023. This tool is based directly on the IMF’s Debt Sustainability Framework for Market-Access Countries, released in 2021, and is relevant only for countries that “principally receive financing through market-based instruments and on non-concessional terms.” Through extensive testing, the IMF developed a model that measures the probability of a borrowing country experiencing sovereign debt strains in the near-term based on changes in nine macroeconomic and governance variables.
Results
Among middle- and lower-income countries with market access with full data availability across all indicators, Argentina, Angola, and Pakistan are most at risk of sovereign debt stress. In the heatmap below, brighter colors indicate more risk, while darker colors indicate less risk. I use percentile scoring for each variable, including the probability of sovereign stress outcome.
Argentina defaulted on local currency debt in 2023, which penalized the country via the “stress history” indicator and propelled it into the “top” spot. The sovereign defaults that I tallied based on S&P for 2023 are El Salvador, Cameroon, and Ethiopia on foreign currency debt and Argentina, Ghana, El Salvador, Mozambique, and Sri Lanka on local currency. Let me know if I am missing any!
Caveats
Regarding the other 2023 sovereign defaults, El Salvador registered as sixth-most at risk of sovereign stress. I would expect Sri Lanka to rank fairly high on the sovereign stress heat-map above. But data for Sri Lanka has been patchy since its 2022 default, preventing me from making a full calculation on the same footing as other countries.
The IMF does not consider Cameroon, Ethiopia, Ghana, and Mozambique to currently be MACs. Other countries are borderline. For instance, Angola has been a market-access country for several years, but it seems like the IMF is in the process of declassifying it due to current vulnerabilities. So I may remove Angola from the next update. On the other hand, Nigeria still seems to be within the IMF’s MAC perimeter.
Also, this tracker shouldn’t be taken as gospel as to the likelihood of sovereign stress, as it only reflects macroeconomic-related indicators and which are mostly backward-looking. It fails to capture the qualitative aspects of a government’s commitment to reforms. Case in point: I wrote of Egypt’s brightening prospects last week.
Changes since October 2023
The table below outlines changes in the ten MACs most at-risk of experiencing sovereign debt strains. Argentina, Nigeria, and Ukraine have deteriorated by climbing up the ranking. Angola, Pakistan, Egypt, Jordan, Ecuador, Belize, and Mexico have seen their rankings improve. El Salvador continues to occupy the sixth spot.
| Rank | May 2024 | October 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| 🥇 | 🇦🇷 Argentina ⬆️ | 🇦🇴 Angola |
| 🥈 | 🇦🇴 Angola ⬇️ | 🇵🇰 Pakistan |
| 🥉 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan ⬇️ | 🇪🇬 Egypt |
| 4 | 🇪🇬 Egypt ⬇️ | 🇯🇴 Jordan |
| 5 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria ⬆️ | 🇦🇷 Argentina |
| 6 | 🇸🇻 El Salvador | 🇸🇻 El Salvador |
| 7 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine ⬆️ | 🇪🇨 Ecuador |
| 8 | 🇯🇴 Jordan ⬇️ | 🇧🇿 Belize |
| 9 | 🇪🇨 Ecuador ⬇️ | 🇩🇴 Dominican Republic |
| 10 | 🇧🇿 Belize ⬇️ | 🇲🇽 Mexico |
I was surprised to see Mexico in October’s top ten, which points to some of this tool’s analytical limits. I and many others have generally perceived Mexico as a positive EM story in recent years, with an economy benefiting from supply chain reconfigurations and near-shoring, and an appreciating peso. Nevertheless, this IMF model can help challenge consensus narratives: in fact, Mexico is penalized precisely because of the strong appreciation of its real effective exchange rate over the past three years.